Which Regulatory Acts are Involved
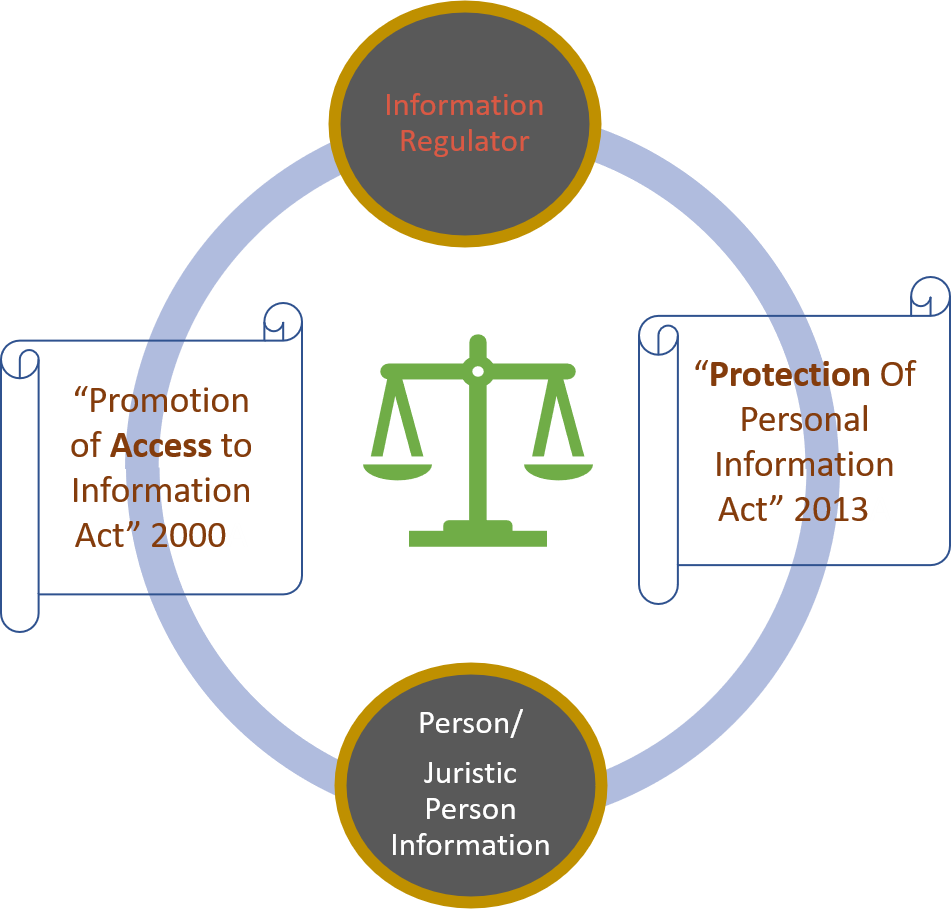
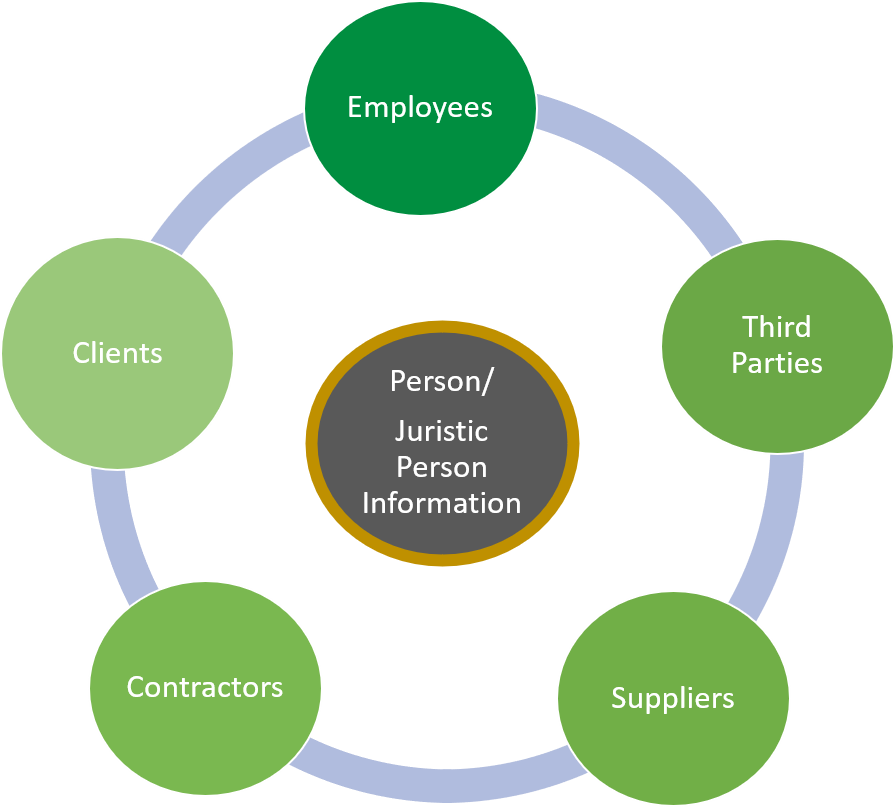
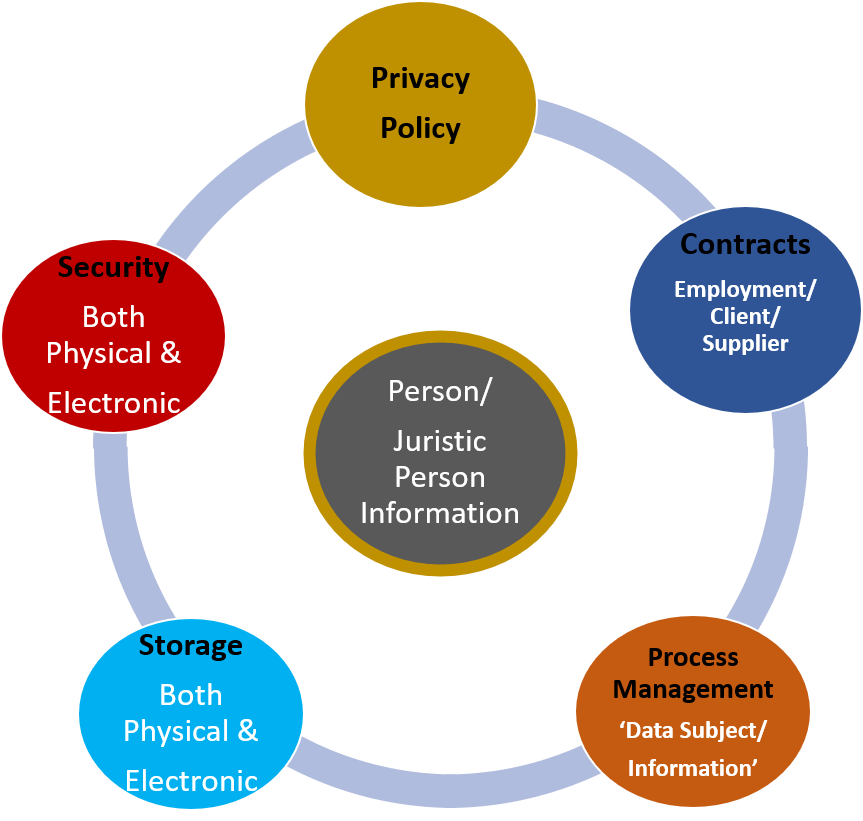
The South African POPI Act is a comprehensive piece of legislation that is designed to regulate the processing of personal information by organizations. The Act is based on international data protection laws and principles, such as the European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), and seeks to protect the privacy rights of individuals in South Africa. Under the POPI Act, organizations are required to obtain the consent of individuals before collecting and processing their personal information. They must also ensure that personal information is accurate, up-to-date, and only used for lawful purposes.
In addition to the POPI Act, there are other regulatory acts and laws in South Africa that are relevant to data protection and privacy. The Electronic Communications and Transactions (ECT) Act is one such law that provides guidance on electronic communications and transactions. The ECT Act defines the legal requirements for electronic transactions and signatures, and includes provisions for the protection of personal information in electronic form.
Another important law is the Promotion of Access to Information Act (PAIA). This act regulates access to information held by public and private bodies and provides a mechanism for individuals to access their personal information that is held by organizations. The PAIA ensures that individuals have the right to access and rectify their personal information, and that organizations must provide access to such information within a reasonable time frame.
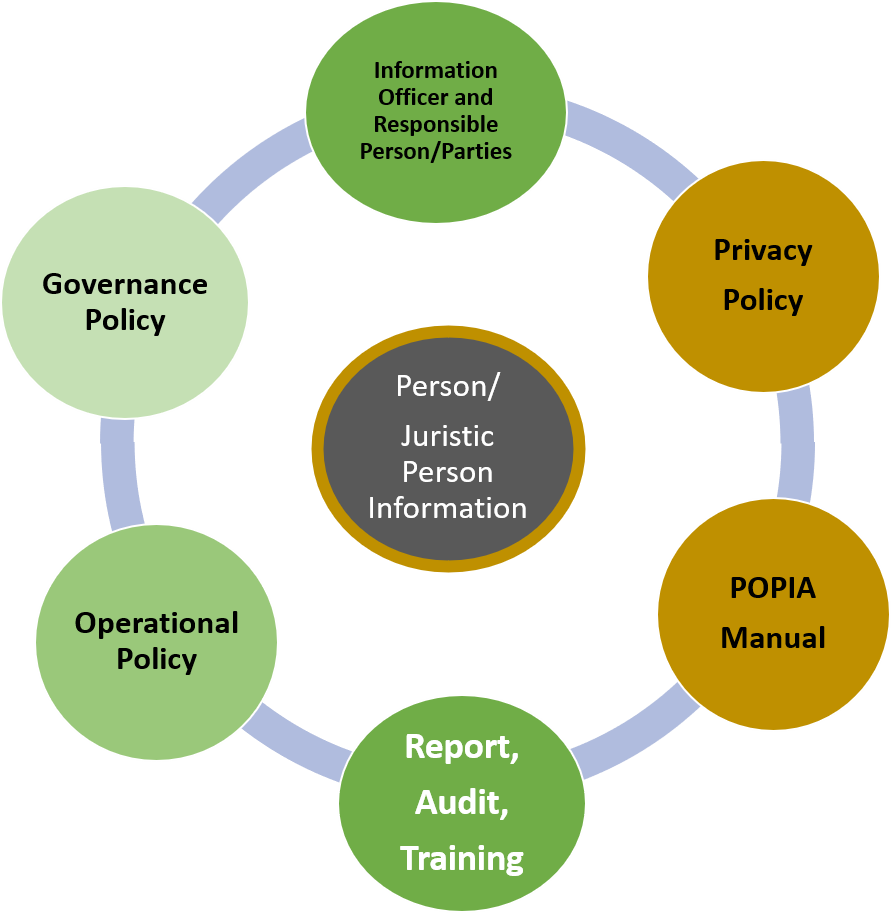
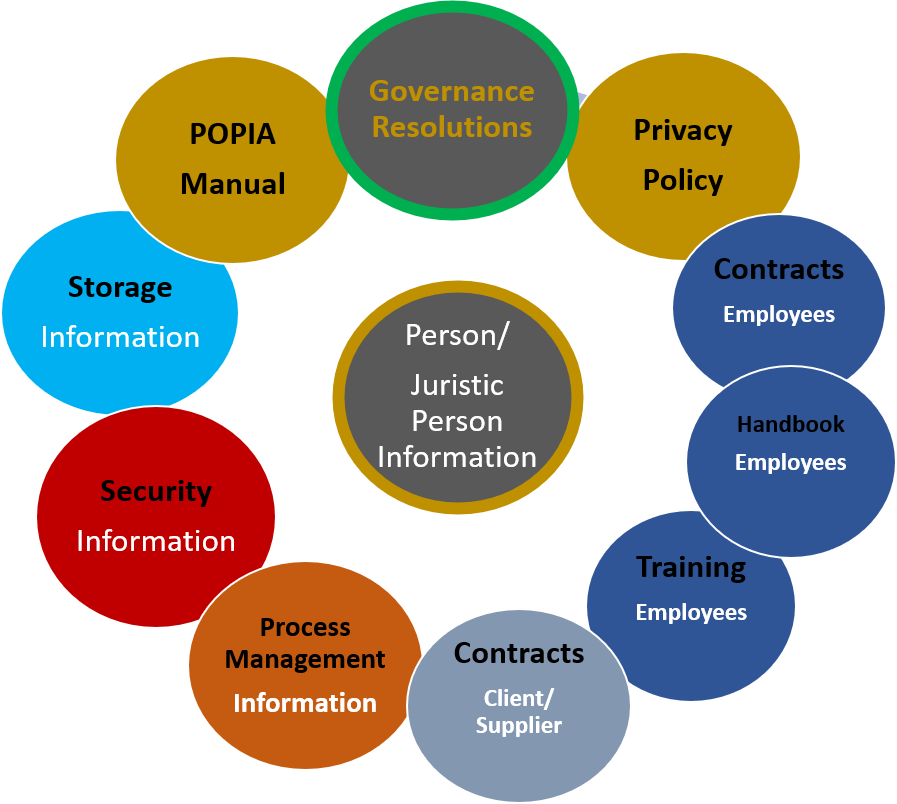
The POPI Act works in conjunction with these other laws to provide a comprehensive legal framework for data protection and privacy in South Africa. Organizations that handle personal information must comply with all of these laws to ensure that they are processing personal information lawfully and responsibly. Failure to comply with these laws can result in significant legal and reputational consequences for organizations. Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to understand and adhere to the provisions of these regulatory acts to protect the privacy rights of individuals in South Africa.